en.wikipedia.org
Always private
DuckDuckGo never tracks your searches.
Learn MoreYou can hide this reminder in Search Settings
All regions
Argentina
Australia
Austria
Belgium (fr)
Belgium (nl)
Brazil
Bulgaria
Canada (en)
Canada (fr)
Catalonia
Chile
China
Colombia
Croatia
Czech Republic
Denmark
Estonia
Finland
France
Germany
Greece
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India (en)
Indonesia (en)
Ireland
Israel (en)
Italy
Japan
Korea
Latvia
Lithuania
Malaysia (en)
Mexico
Netherlands
New Zealand
Norway
Pakistan (en)
Peru
Philippines (en)
Poland
Portugal
Romania
Russia
Saudi Arabia
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
South Africa
Spain (ca)
Spain (es)
Sweden
Switzerland (de)
Switzerland (fr)
Taiwan
Thailand (en)
Turkey
Ukraine
United Kingdom
US (English)
US (Spanish)
Vietnam (en)
Safe search: moderate
Strict
Moderate
Off
Any time
- Was this helpful?
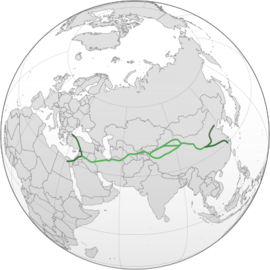
- The Silk Road [a] was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. [1] Spanning over 6,400 km (4,000 mi), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds. [2] [3] [4] The name "Silk Road" was coined in the late 19th century, but some 20th- and 21st ...
britannica.com
Nov 27, 2024Silk Road, ancient trade route, linking China with the West, that carried goods and ideas between the two great civilizations of Rome and China. Silk went westward. Wools, gold, and silver went east. China also received Nestorian Christianity and Buddhism (from India) via the route. Read more about the Silk Road here.Author:The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannicahistory.com
The Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting China and the Far East with the Middle East and Europe. Established when the Han Dynasty in China officially opened trade with the West in ...worldhistory.org
World History Encyclopedia
https://www.worldhistory.org › Silk_Road
The Silk Road was a network of ancient trade routes, formally established during the Han Dynasty of China in 130 BCE, which linked the regions of the ancient world in commerce between 130 BCE-1453 CE. The Silk Road was not a single route from east to west and so historians favor the name 'Silk Routes', though 'Silk Road' is commonly used.education.nationalgeographic.org
National Geographic Education
https://education.nationalgeographic.org › resource › silk-road
Dec 5, 2024The Silk Road is neither an actual road nor a single route. The term instead refers to a network of routes used by traders for more than 1,500 years, from when the Han dynasty of China opened trade in 130 B.C.E. until 1453 C.E., when the Ottoman Empire closed off trade with the West.discovermagazine.com
Mar 14, 2023Commonly called the Silk Road, this terrestrial and aquatic system spanned as many as 6,000 miles and connected countless territories, from China and India to Iran and Italy. Crossing through the toughest terrains, including mountains, deserts, steppes and seas, the system cut from China's ancient capital city of Chang'an ( Xi'an) to ...geeksforgeeks.org
GeeksForGeeks
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org › silk-road
Jan 29, 2024The Silk Road was a network of commercial routes that linked the East and West from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. The Roman Empire and China, as well as subsequent medieval European countries, traded heavily along the Silk Road. The Silk Road united the continents of Europe, Africa, and Asia via limnic, marine, and overland routes.en.unesco.org
The Great Silk Road is a system of caravan routes of ancient times and in the Middle Ages which connected Asia with the Mediterranean and European world. These routes highly influenced the development of trade interactions and cultural ties between the West and the East. The Silk Road served not only as route for exporting goods such as silk, spices, precious metals, minerals handicrafts ...silk-road.com
Silk Road
https://silk-road.com
The Silk Road is named after the lucrative international trade in Chinese silk textiles that started during the Han dynasty (207 BC - 220 CE). Using one single name for this intricate web of trade routes is a modern invention; the name Silk Road was coined by the geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen in the late 19th century. ...chinahighlights.com
China Highlights
https://www.chinahighlights.com › silkroad › history.htm
Mar 13, 2024The Silk Road is the world's longest and most historically important overland trade route. Trade began thousands of years ago because the tradesmen found that ferrying products was profitable, and silk was one of the main trade items. Through trade and travel along the road, the cultures throughout Eurasia developed economically ...Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Help us improve DuckDuckGo searches with your feedback